Basic Usage
July 23, 2023About 4 min
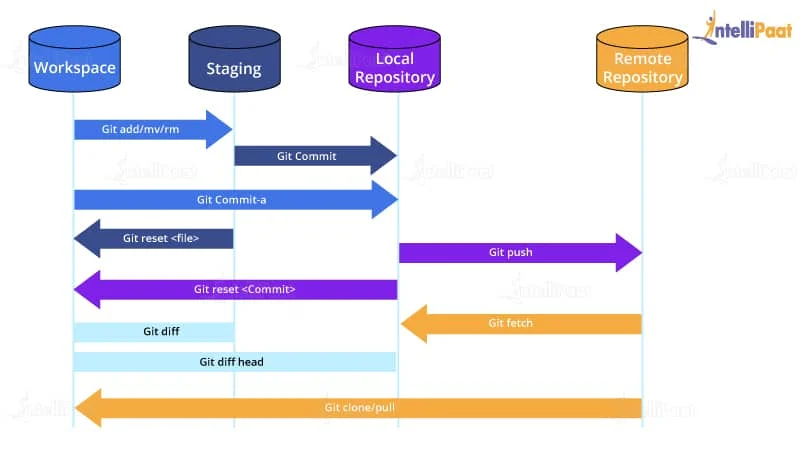
The structure of git
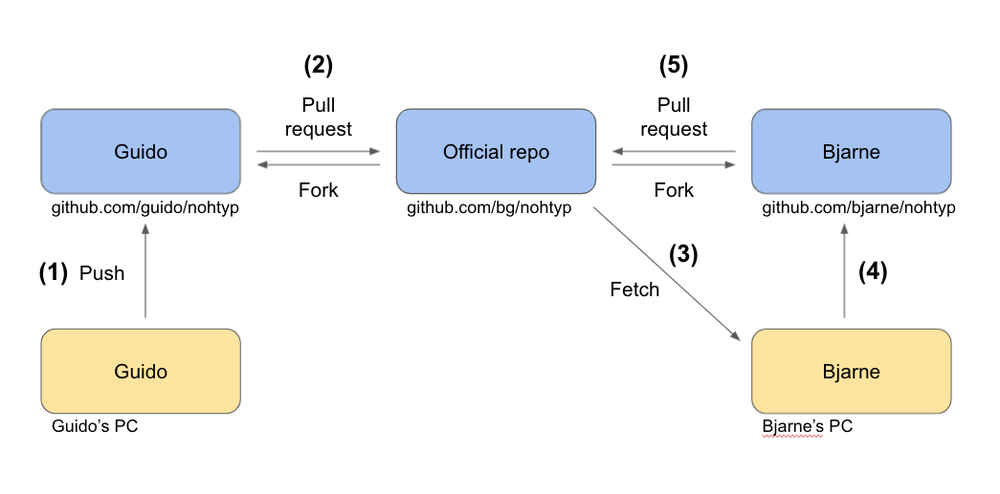
Collaboration
Git Code Hosting Center
Git basic operation
git init
#初始化本地库(创建.git目录,并创建本地库相关内容和文件)
git init
#设置签名(项目级别)
# tom/email 注意:这里的签名和登录远程库无任何关系
# 作用:区分不同开发人员的身份
git config user.name tom_pro
git config user.email good@mail.com
#设置签名(系统级别)
# tom/email 注意:这里的签名和登录远程库无任何关系
# 作用:区分不同开发人员的身份
git config --global user.name tom_pro
git config --global user.email good@mail.com
#优先级说明
# 1. 项目级别/仓库级别:仅在当前本地库生效【优先级最高】
# 2. 系统用户级别:当前操作系统用户范围生效
#项目签名保存目录
# .git/config
#系统签名保存目录
#~/.gitconfigstatus and log
#本地库状态
git status
#添加到缓存区
git add filename.ext
#删除缓存区文件
git rm --cached filename.ext
#提交到本地库
git commit filename.ext -m "Comments for the committed file"
#查看提交信息
git log
#查看提交信息,每条日志显示一行
git log --pretty=oneline
#查看提交信息,每条日志显示一行,hash值部分显示
git log --online
#查看提交信息,每条日志显示一行,并存在指针(HEAD)移动不同版本所需步数
git reflogversion switch
#reset命令参数对比
# 1. --soft: 只在本地库移动HEAD指针
# 2. --mixed:本地库移动HEAD指针/并重置暂存区
# 3. --hard: 本地库移动指针/重置暂存区/重置工作区
#git reset --hard 索引值或局部索引值
git reset --hard 7bf0e31
#该方式只可以后退
#后退一步
git reset --hard HEAD^
#后退三步(n个^后退n布)
git reset --hard HEAD^^^
#指定后退步数
git reset --hard HEAD~3compare
#工作区和暂存区文件比较
git diff filename
#工作区和本地库文件比较
git diff HEAD filename
#工作区和本地库历史版本文件比较
git diff HEAD^ filename
#不增加文件名称,对比所有差异文件
git diffbranch
#查看分支
git branch -v
#创建新分支hot_fix
git branch hot_fix
#切换分支
git checkout hot_fix
#合并分支
# 切换至接受合并的分支
git checkout master
# 合并hot_fix分支至master分支中
git merge hot_fixconflict
#当合并产生冲突时,分支进入到解决冲突状态,编辑冲突文件,内容如上图所示,
#之后将冲突文件编辑至理想状态后,之后将文件标记为已解决状态
#最后提交合并
#1. 标记文件为解决状态
git add conflict.file
#2. 提交合并文件(冲突解决状态下,不可以添加文件名称)
git commitremote
#添加远程源
#git remote add [远程分支名称] [远程地址]
git remote add origin https://github.com/seamice/periodic.git
#推送至远程库
#git push [远程分支名称] [需推送分支]
git push origin master
#克隆远程库
git clone https://github.com/seamice/periodic.git
#列出分支文件(可以更改ls-tree相关参数更改输出内容样式)
git ls-tree -r --name-only sat_down/master
#查看所有远程分支
git branch -r
#检出远程的feature-branch分支到本地
git checkout -b feature-branch origin/feature-branch
#创建并切换到分支feature-branch
git checkout -b feature-branch
#推送本地的feature-branch(冒号前面的)分支到远程origin的feature-branch(冒号后面的)分支(没有会自动创建)
git push origin feature-branch:feature-branchfetch and pull
#抓取远程库并和本地库融合
# pull命令效果是fetch + merge
git pull origin master
#抓取远程库origin master分支
git fetch origin master
#切换至远程分支
git checkout origin/master
#切换至本地分支
git checkout master
#合并至本地master
git merge origin/masterCreate new branch
# --orphan creates a new branch, but it starts without any commit. After running the above command you are on a new branch "NEWBRANCH", and the first commit you create from this state will start a new history without any ancestry.
#You can then start adding files and commit them and they will live in their own branch. If you take a look at the log, you will see that it is isolated from the original log.
git checkout --orphan NEWBRANCH
git rm -rf .Delete branch
# Delete local branch
git branch --delete name
# delete remote branch
git push remote --delete nameRename branch
# rename local branch
git branch -m oldname newname